lung cancer
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths among men worldwide. It is strongly associated with cigarette smoking, but other factors like secondhand smoke, pollution, and occupational exposure to chemicals also play a role.
Key Points:
Major Cause: Smoking remains the top cause, responsible for nearly 85–90% of cases.
Common Symptoms: Persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, and coughing up blood.
Risk Factors: Long-term tobacco use, exposure to asbestos, radon gas, and family history of lung cancer.
Prevention: Avoid smoking, limit exposure to harmful chemicals, maintain a healthy diet, and go for regular health checkups.
Early Detection Matters: Many men are diagnosed at advanced stages, making treatment more difficult. Regular screenings for high-risk individuals can save lives.
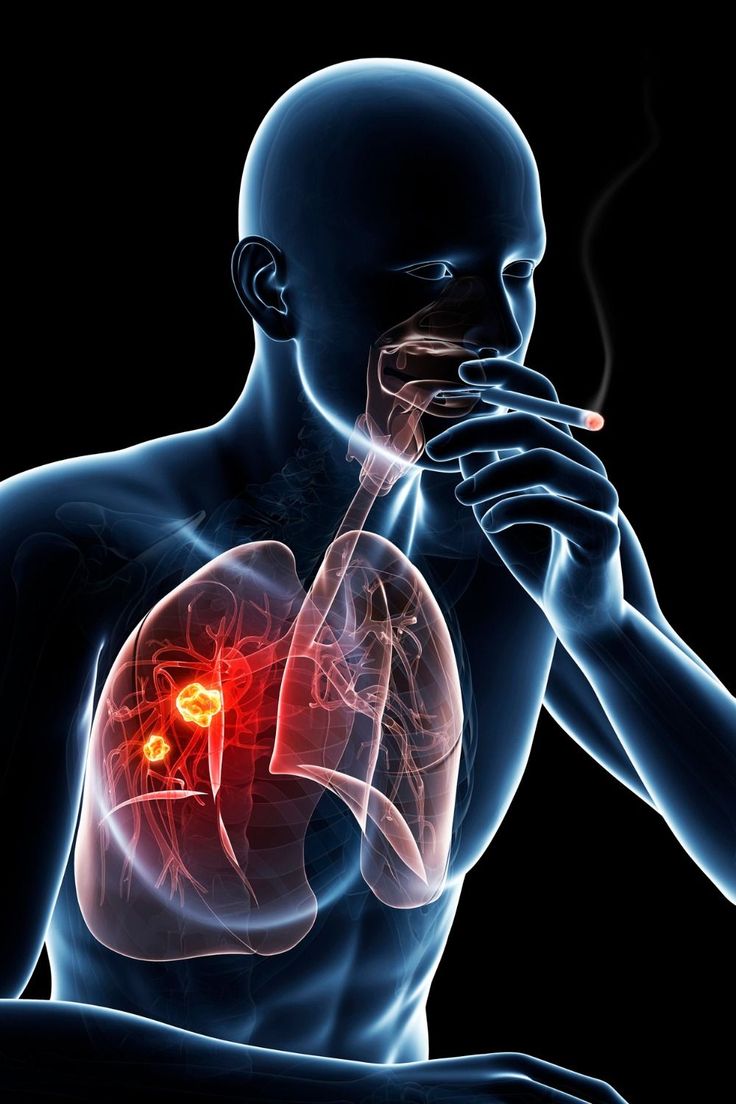
Lung cancer continues to be one of the most serious health challenges faced by men today. It often develops silently, with symptoms appearing only in later stages. Smoking remains the biggest risk factor, but even non-smokers can be affected due to pollution, occupational hazards, or genetic factors.
Key Highlights:
Warning Signs: Long-lasting cough, chest pain, repeated lung infections, shortness of breath, and unexplained fatigue.
High-Risk Groups: Men who smoke, work in chemical industries, or have a family history of lung cancer.
Why Men Are More Vulnerable: Higher smoking rates, exposure to workplace toxins, and lower participation in regular health screenings.
Prevention Steps: Quit smoking, use protective masks in polluted or chemical-heavy environments, and get routine medical checkups.
Early Action Saves Lives: Detecting lung cancer at an early stage greatly improves survival and treatment outcomes.
Lung cancer is one of the most common and deadliest cancers among men. The major cause is smoking, but exposure to air pollution, chemicals, and family history can also increase risk.
Symptoms to Watch For:
Persistent cough or chest pain.
Shortness of breath.
Coughing up blood.
Unexplained weight loss.
Prevention:
Quitting smoking, avoiding secondhand smoke, wearing protection in workplaces with chemicals, and going for regular checkups can help reduce the risk. Early detection improves the chances of successful treatment.